Smart Farming: The Power of IoT in Agriculture
The global population is growing, and the demand for food is increasing at an unprecedented rate. To meet this challenge sustainably and efficiently, the agricultural sector is turning towards innovative technologies. Among these, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands out as a game-changer, transforming traditional farming practices into a more data-driven and optimized approach. This article delves into the world of IoT in Agriculture, exploring its benefits, applications, challenges, and the exciting future it holds for the farming industry.
What is IoT in Agriculture?
At its core, IoT in Agriculture, also known as smart farming or precision agriculture, involves the use of interconnected devices, sensors, software, and analytics to collect, monitor, and analyze data related to various aspects of agricultural operations. This data-driven approach empowers farmers to make informed decisions, automate processes, improve yields, reduce waste, and ultimately enhance the overall efficiency and sustainability of their farms.
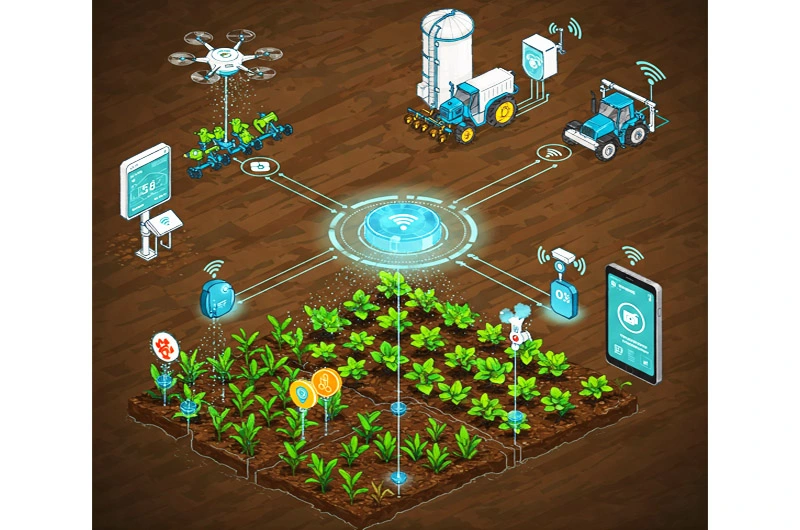
Key Benefits of Implementing IoT in Agriculture:
Integrating IoT technologies into farming practices offers a multitude of advantages:
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Automation of tasks like irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on real-time data, significantly improves efficiency and boosts crop and livestock yields.
- Optimized Resource Management: IoT sensors can precisely monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and weather conditions, allowing for optimized use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Improved Crop and Livestock Health: Continuous monitoring of environmental factors and animal health metrics enables early detection of diseases, pests, and nutritional deficiencies, allowing for timely interventions and preventing significant losses.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data insights provide farmers with a comprehensive understanding of their operations, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding planting, harvesting, resource allocation, and overall farm management.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By optimizing resource usage, minimizing waste, and automating tasks, IoT helps in significantly reducing operational costs for farmers.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Precision agriculture practices driven by IoT contribute to sustainable farming by minimizing the use of chemicals, conserving water, and improving soil health.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Farmers can remotely monitor their fields and livestock, and even control certain operations through connected devices, saving time and effort.
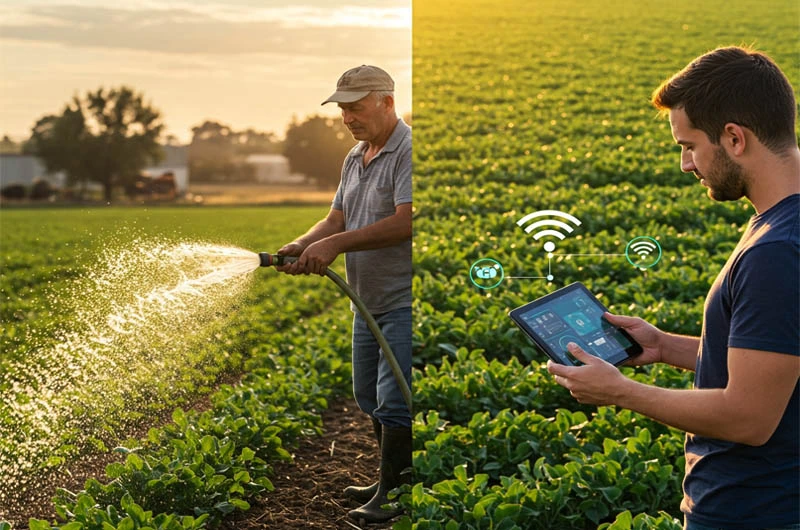

Applications of IoT in Agriculture: Real-World Examples
The applications of IoT in agriculture are diverse and constantly evolving. Here are some prominent examples:
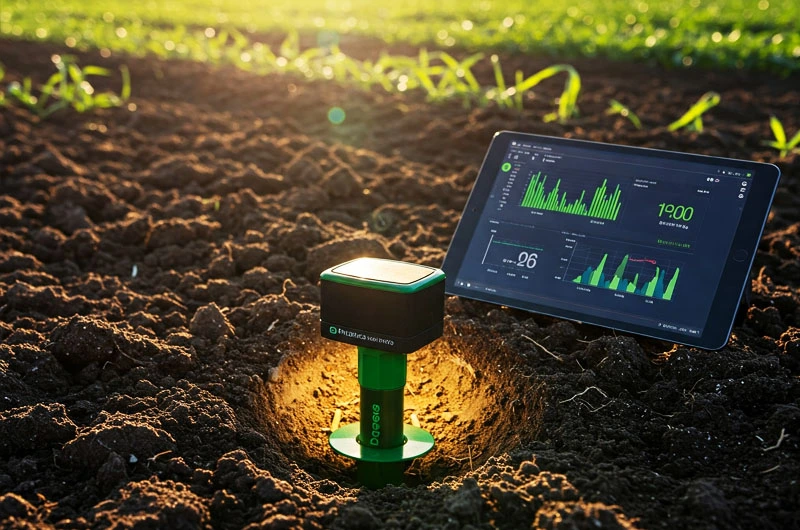
Precision Crop Farming:
- Soil Monitoring: Sensors collect data on soil moisture, temperature, pH levels, and nutrient content, providing insights for optimized irrigation and fertilization.
- Weather Monitoring: Smart weather stations provide real-time and hyperlocal weather data, aiding in planning and risk management.
- Yield Monitoring: Sensors on harvesting equipment collect data on crop yield, allowing for analysis and optimization of future planting strategies.
- Drone Technology: Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can capture aerial images of fields, providing valuable data on crop health, growth patterns, and potential issues.

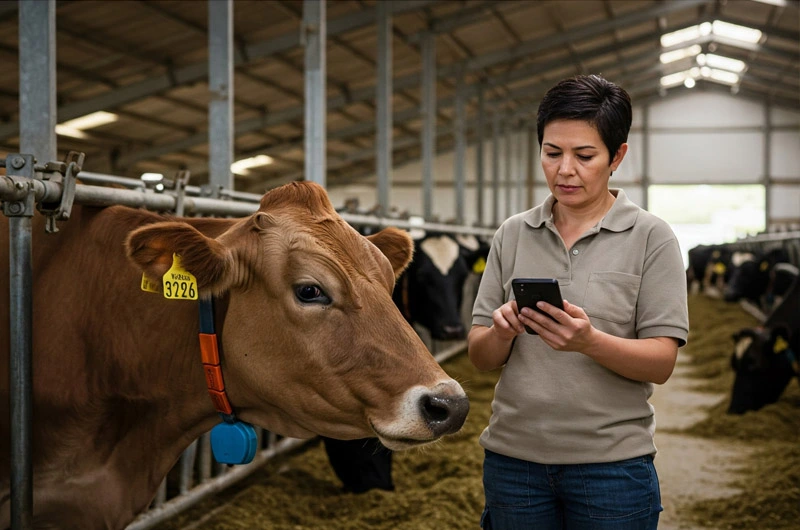
Smart Livestock Management:
- Animal Tracking: GPS-enabled tags allow farmers to track the location and movement of their livestock, improving grazing management and preventing theft.
- Health Monitoring: Wearable sensors monitor vital signs like body temperature, heart rate, and activity levels, enabling early detection of illnesses.
- Automated Feeding and Watering: Smart systems can automatically dispense feed and water based on the specific needs of the animals.

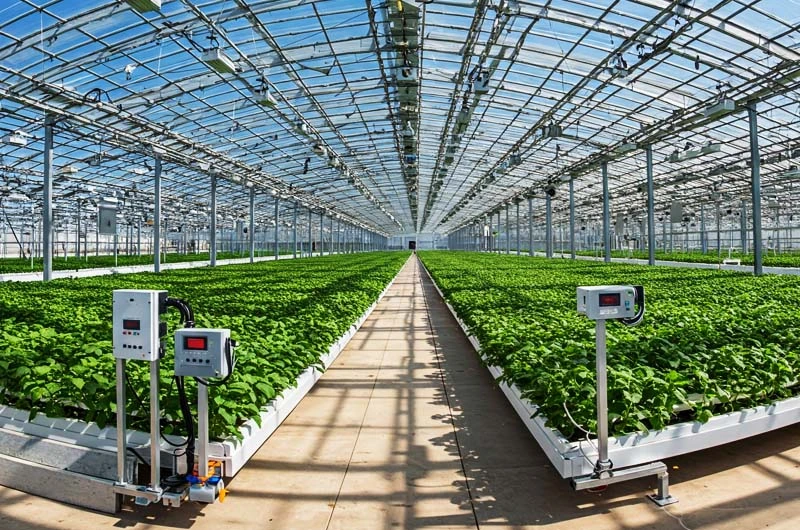
Smart Greenhouses:
- Climate Control: Sensors monitor and automatically adjust temperature, humidity, light levels, and ventilation within greenhouses to create optimal growing conditions.
- Automated Irrigation and Nutrient Delivery: IoT systems can precisely control the delivery of water and nutrients to plants in greenhouses.

Farm Automation:
- Autonomous Tractors and Machinery: Self-driving tractors and other agricultural machinery can perform tasks like plowing, planting, and harvesting with greater precision and efficiency.
- Robotics for Harvesting and Weeding: Robots equipped with computer vision can identify and selectively harvest ripe crops or remove weeds, reducing labor costs.
Challenges in Implementing IoT in Agriculture:
While the potential of IoT in agriculture is immense, there are certain challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption:
- High Initial Investment Costs: The cost of sensors, devices, software, and infrastructure can be a significant barrier for small and medium-sized farmers.
- Connectivity Issues: Reliable internet connectivity, especially in rural areas, is crucial for the functioning of IoT devices.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Protecting the vast amounts of data collected by IoT devices from cyber threats is paramount.
- Lack of Technical Expertise: Farmers may require training and support to effectively use and maintain IoT technologies.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between different devices and platforms can be challenging.
- Power Availability: Reliable power supply is essential for the continuous operation of IoT devices in remote agricultural locations.
The Future of IoT in Agriculture: Trends to Watch
The future of IoT in agriculture is bright, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
- Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: AI-powered analytics will play a crucial role in processing and interpreting the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices, providing even more valuable insights and predictions.
- Integration of 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable connectivity, enabling the deployment of more advanced IoT applications.
- Rise of Robotics and Automation: We will see wider adoption of robots for various agricultural tasks, further increasing efficiency and reducing labor dependence.
- Focus on Sustainability: IoT will play a key role in promoting sustainable farming practices and reducing the environmental footprint of agriculture.
- Growth of Vertical and Urban Farming: IoT technologies will be instrumental in optimizing controlled environment agriculture in urban settings.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Combining IoT with blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and traceability of agricultural products, ensuring food safety and building consumer trust.
IoT in Agriculture is no longer a futuristic concept but a tangible reality that is revolutionizing the way we grow our food. By leveraging the power of interconnected devices and data analytics, farmers can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. While challenges remain, the continuous advancements in technology and decreasing costs are paving the way for a wider adoption of IoT in the agricultural sector, promising a more secure and sustainable food future for all. Embrace the power of smart farming – the future of agriculture is connected.

